Troubleshooting Schneider 140DDI Input Modules: A Field Guide
The Role of External 24 VDC Field Power
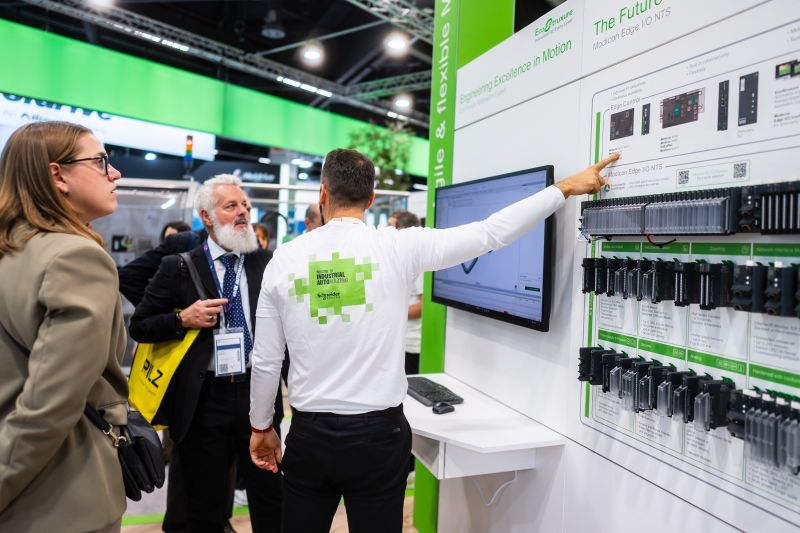
The Schneider Electric 140DDI digital input module serves as a cornerstone for the Quantum PLC series. It facilitates reliable data acquisition from field devices like limit switches and sensors. You will commonly find these modules in demanding environments such as oil refineries and pharmaceutical plants. However, engineers often face a specific challenge: all input LEDs remaining dark. This guide explores why this happens and how to restore system functionality quickly.
Unlike some basic controllers, the 140DDI does not provide internal power for field signals. Each channel requires an external 24 VDC source to function. If you notice all LEDs are off, the PLC logic is rarely the culprit. Instead, the issue usually stems from the field-side electrical circuit. A single tripped circuit breaker or a blown fuse can disable an entire module. Consequently, technicians must verify the voltage at the common (COM) terminal before replacing hardware.

Distinguishing Backplane from Field Power Circuits
The Quantum architecture utilizes a sophisticated split-power design to protect sensitive electronics. The backplane powers the internal logic and communication, while the field supply handles the actual signal detection. Therefore, a module can appear “Healthy” or “Online” in EcoStruxure Control Expert even if the inputs are dead. This separation enhances safety but frequently misleads inexperienced maintenance staff during initial commissioning phases.
Managing Industrial Noise and Grounding Integrity
High-performance industrial automation requires clean electrical signals to prevent false triggering. While the 140DDI features robust noise immunity, poor wiring practices can compromise its performance. Floating commons or shared grounds with high-load motors often cause signal instability. In my experience at Powergear X Automation, ensuring a dedicated ground for DC signals significantly reduces intermittent data errors. Proper shielding and polarity management are essential for long-term system reliability.
Maintenance Best Practices for Harsh Environments
Facilities in the mining or heavy manufacturing sectors subject hardware to extreme vibrations. Over time, screw terminals can loosen, leading to intermittent signal loss. We recommend transitioning to spring-clamp terminal blocks where the environment allows. Additionally, implementing strain relief for heavy cable bundles prevents physical damage to the module connectors. Regular inspections during scheduled shutdowns ensure that the COM jumpers remain secure and conductive.
Expert Analysis by Powergear X Automation
The longevity of the Quantum series proves Schneider Electric’s commitment to industrial durability. However, as these systems age, the quality of the external power distribution becomes the weakest link. At Powergear X Automation, we believe that proactive power monitoring is better than reactive troubleshooting. Integrating a “Power OK” signal from your field supply into your PLC logic can save hours of diagnostic time. If you require high-quality components or technical support for your control systems, visit Powergear X Automation for expert solutions.
Technical Implementation Checklist
- ✅ Measure voltage directly between the input terminal and the common point.
- ✅ Verify that the module configuration in the software matches the physical hardware.
- ✅ Inspect all external fuses and miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) feeding the rack.
- ✅ Tighten all terminal connections to the manufacturer’s specified torque settings.
- ✅ Confirm that the 24 VDC polarity aligns with the module’s wiring diagram.
Industrial Application Scenarios
Oil & Gas: Monitoring emergency shutdown (ESD) interlocks across remote wellhead sites.
Pharmaceuticals: Tracking valve positions in sterile batch processing environments to ensure safety.
Manufacturing: Integrating high-speed limit switches on assembly lines for precise motion control.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How do I determine if the 140DDI module itself has failed?
If you confirm 24 VDC is present at the input terminals but the PLC registers no data, check the backplane status. If the “Active” LED is on but no inputs respond to a known live signal, the internal optocouplers may be damaged.
Q2: Can I mix different voltage types within the same Quantum I/O rack?
Yes, the Quantum backplane supports various modules. However, you must maintain physical separation between AC and DC field wiring. Mixing these in the same conduit can cause electromagnetic interference and lead to erratic signal behavior.
Q3: What should I prioritize when purchasing a replacement 140DDI module?
Verify the hardware revision and firmware compatibility with your existing CPU. It is also wise to check the condition of the terminal blocks. Buying from a reputable partner like Powergear X Automation ensures you receive tested, reliable components for your critical infrastructure.